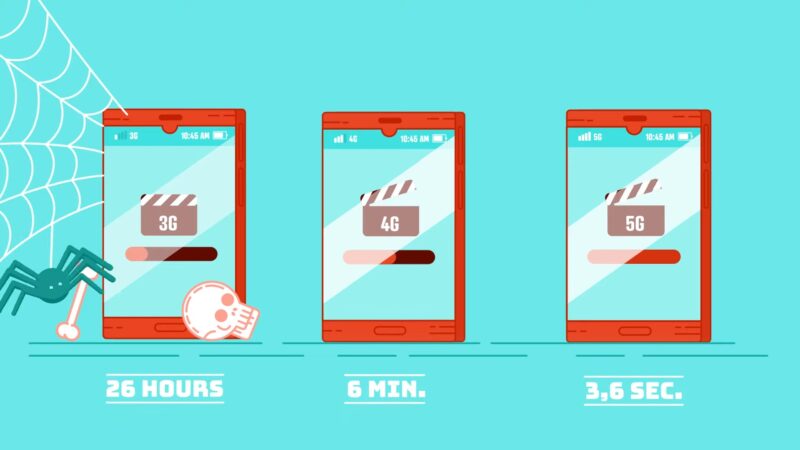
As the fifth generation of wireless technology, 5G is an exciting new development that will impact the way data is transmitted over cellular networks. Multiple telecom providers are already working hard to roll out new 5G infrastructure and global competition is heating up as China has made substantial investments in exporting the technology. Much of the excitement is justified given the vast potential of 5G use cases.[
What distinguishes 5G from previous generations is its ability to utilize multiple frequency bands of the wireless spectrum. Existing technology relies on the low-band spectrum, which provides both a broad coverage area and effective signal penetration. Unfortunately, the massive number of wireless communications has left this band crowded and slow. Even under ideal conditions, data speeds on the low-band top out around 100 Mbps.
The mid-band spectrum provides greater speed and can cover an area quickly, though not as broadly as low-band signals. This spectrum doesn’t penetrate buildings very well, but it does deliver speeds around 1 Gbps. Since 5G can transmit over multiple bands, some mobile carriers (Sprint, specifically) have emphasized the mid-band spectrum to serve as the backbone of their 5G services.
Finally, there’s the high-band spectrum, which delivers blindingly fast speeds of up to 10 Gbps with extremely low latency. The problem, however, is that transmissions are very narrow and not effective at penetrating buildings. One of the great innovations of 5G will be its ability to leverage multiple spectrum bands to expand coverage and provide targeted, high-performance connectivity when the conditions are right for it.
What Can 5G Do?
Quite simply, 5G technology will allow cellular networks to do everything they already do now, only faster and more reliably. As 5G networks continue to roll out, wireless services will become more seamless and effective. Greater volumes of data will be able to be transmitted with minimal delay, and it will be easier to provision computing resources remotely.
Under most conditions, 5G speed is expected to match or even exceed that of physical fiber-optic connections. Network congestion will also become a thing of the past since 5G can accommodate and support as up to 1 million connected objects per square mile. This combination will make 5G critical to the future success of Internet of Things (IoT) devices.
Five 5G Use Cases and What They Could Mean for the Future of Your Network
1. Expanded Industrial IoT
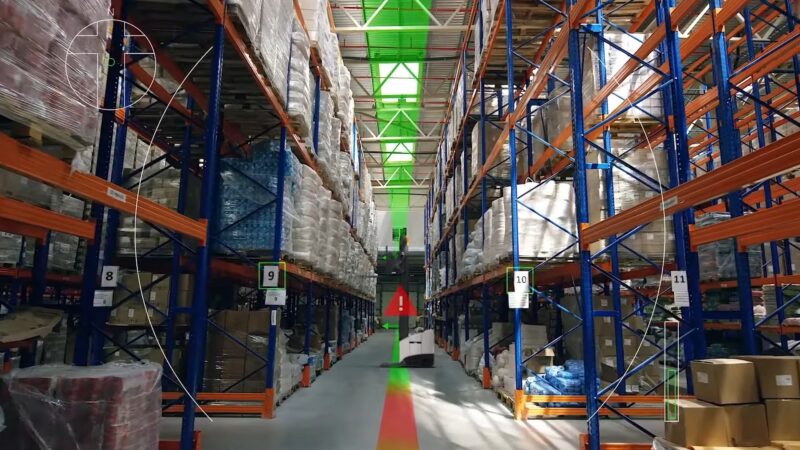

Manufacturers are already making extensive use of IoT sensors to monitor performance and optimize both production and logistics. Lower latency and increased wireless flexibility will allow them to further streamline their infrastructure, build interconnected and semi-automated smart factories, and increase visibility throughout their supply chains.
2. More Real-Time Data for Better Decisions

Whether it’s a retail environment, a power utility grid, or a healthcare facility, 5G can provide reliable data in real-time that can help an organization make better decisions. Because it can transmit so much information so quickly, a 5G network can gather and process data from multiple sources so people can actually see and address potential issues as they’re happening rather than trying to determine what went wrong after the fact. This allows for rapid optimization and dynamic decision-making that reflects the reality on the ground.
3. Autonomous Vehicles
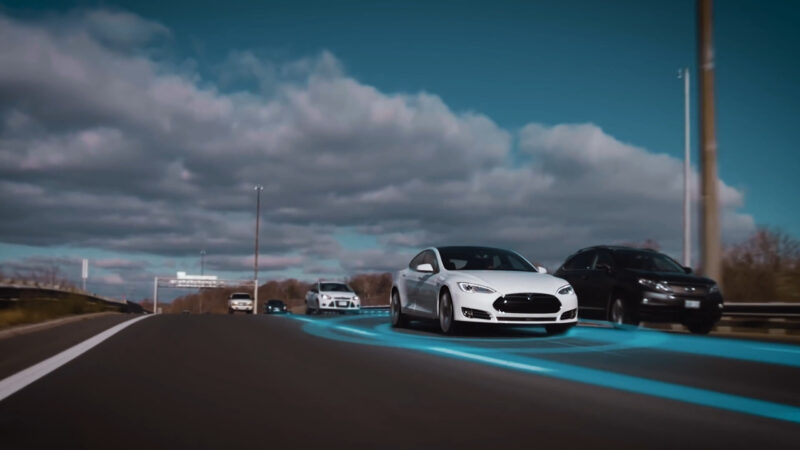

Self-driving cars may not quite be here in large numbers just yet, but the lack of a powerful 5G network is one of the reasons why they’re not a more common sight on the road. Since 5G is especially effective at transmitting data between moving objects, it will be absolutely essential to the success of autonomous vehicle networks, which will need to deliver huge amounts of information between vehicles.
Other connectivity needs like remote diagnostics, operating system updates, predictive maintenance, in-car payments, and fleet management will be difficult to scale without the power of 5G networks.
4. Smart City Applications
Another exciting application for 5G is smart city technology. Cities around the world are experimenting with digital solutions that could minimize traffic congestion, improve safety, and make public services more efficient. Smart IoT sensors could potentially transmit data quickly over 5G networks to alert city officials of problems, notify commuters of traffic conditions, or even notify people of open parking spaces.
5. Improved Healthcare Networks
Few industries are more poised for a technology-induced disruption than the healthcare sector. Data limitations have long presented an obstacle to healthcare interoperability, but 5G networks could make it possible for high-resolution images to be transmitted quickly and easily between providers.
The increased capacity of 5G networks would be especially beneficial to hospitals, allowing them to expand the use and flexibility of connected IoT devices without compromising performance. Telemedicine services could also be made faster and more reliable through 5G connectivity, especially when it comes to extending those services out to rural areas and other remote locations. Rather than sputtering, grainy video connections, 5G telemedicine could deliver high-quality video streaming to improve patient-physician interactions.
Rolling Out 5G Services
There are a few obstacles that still need to be overcome before 5G services are widely available across the country. Telecom companies are still working to get a handle on managing multi-band networks to find the ideal combination of coverage and speed. The transition to 5G is also quite costly from an infrastructure standpoint. While the investment will likely pay off many times over in the long run, some providers and cities have been slow to invest in new 5G infrastructure when they’re still making use of their 4G infrastructure.
The speed and flexibility of 5G networks will also bring with them a new range of security concerns. New forms of network architecture that take advantage of the technology’s potential may expose themselves to equally innovative cyberattacks. Identifying vulnerabilities and security gaps will be a crucial process in the early days of the 5G rollout if companies and customers are going to be willing to entrust their information to these networks.
FAQ
What is the expected global rollout timeline for 5G?
While many countries have already begun rolling out 5G networks, the global timeline varies. By 2025, it’s expected that most urban areas across the world will have 5G coverage.
How does 5G impact battery life on devices?
Initially, as devices adapt to 5G, there might be a slight decrease in battery life. However, as technology evolves, devices will become more optimized for 5G, potentially leading to improved battery performance.
Is 5G safe for human health?
According to current research and international standards, the radio frequencies used for 5G are safe. However, ongoing research continues to monitor any potential long-term effects.
Will 4G devices work on 5G networks?
While 4G devices won’t be able to access 5G speeds, they will still work on 5G networks, thanks to the network’s backward compatibility.
How will 5G impact the cost of mobile plans?
As with any new technology, there might be a premium for 5G services initially. However, as adoption grows and competition increases, prices are expected to stabilize.
Final Words
The advent of 5G is not just an upgrade from its predecessor; it’s a revolutionary leap that promises to reshape industries, enhance user experiences, and open doors to new technological horizons. As we stand on the cusp of this new era, it’s essential to stay informed and prepared for the transformative changes 5G will bring.
Related Posts:
- 6 Machine Learning Use Cases to Watch in 2023
- Egemen Mustafa Şener's Opinion on Obsolete…
- Cryptocurrency Wallets and Their Role in the NFT Market
- Why – and How – Would a Criminal Lawyer Quit Their Client?
- How Slot Machine Line Configurations Impact Payouts…
- The Game-changing Impact of RFID in Modern Retail








